Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf
A Key Solution For Next Generation Short Haul Optical Fiber Links. By Winston Way, Ph. D. on May 1. 1, 2. Leave a Comment. Conventional 1. G optical fiber transmission systems use binary signal amplitude of 0 light off or 1 light on to convey information. Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf' title='Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf' />Carrierclass, high capacity multiservice access concentrator for legacy and nextgeneration services over fiber or copper SDHSONET, or over PSN. Fluke Networks CertiFiber Pro optical loss test set OLTS certifies two fibers at two wavelengths in three seconds. Optical loss test set featuring Merged Tier 1. Product Brochure Quidway S3300 Switches 1 S3326CHI S3328TPEIMC S3328TPSIEI Product Overview Quidway S3300 switches S3300 for short are nextgeneration. A guide to building serviceoriented networks to differentiate and grow your business Understand the changing landscape of the telecommunications industry and what. Juniper Networks offers highperformance network solutions to help service providers, enterprises the public sector create value accelerate success. Nextgeneration access NGA describes a significant upgrade to the Broadband available by making a step change in speed and quality of the service. Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf' title='Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf' />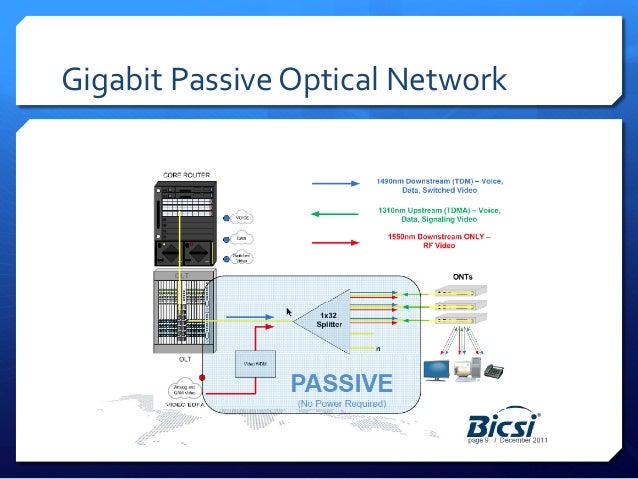 However, as the internet traffic continues to increase at a 2. G and 4. 00. G optical transceivers are needed. At these higher data rates, the bandwidth provided by a binary optical transmitter or receiver can no longer catch up, and therefore starting in 2. Short haul links, such as intra lt 0. As a result, a simple higher order modulation scheme based on pulse amplitude modulation with four amplitude levels termed PAM 4, has been proposed for either intra or inter data center optical links. PAM 4 is a modulation technique whereby 4 distinct pulse amplitudes are used to convey the information. Amplitude levels 1, 2, 3, and 4 are represented by two bits 0. Each pair of bits is called a symbol. When one of the four amplitudes is transmitted in a symbol period, there are two bits transmitted in parallel, therefore the data rate is doubled. In other words, PAM 4 modulation is twice as bandwidth efficient as conventional binary modulation. Although for a fixed bandwidth, PAM 4 enables twice the transmission capacity in comparison to binary modulation, it has to pay a price of a higher required signal to noise ratio SNR. This is because the additional voltage levels with PAM 4 reduce the level spacing by a factor of 3, and therefore PAM 4 is more susceptible to noise than a binary digital signal. Consequently, PAM 4 is normally used for a short haul optical system where a higher SNR can be obtained. This is also the reason why a higher order modulation such as PAM 8, which has 2. Despite the fact that there are many other modulation techniques that can also double or triple the transmission capacity for a fixed bandwidth, PAM 4 modulation has been a leading solution, mainly due to its simplicity and low power consumption, as the most promising modulation technique for 1. G and beyond optical pluggable transceivers for both intra and inter data center optical links, and a strong PAM4 centric ecosystem is forming. For example, electronic PAM 4 chips based on CMOS technology with two channels of 5. Gbs PAM 4 2x. 50. S157342771400126X-gr1.jpg' alt='Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf' title='Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf' />Gbs is available in 2. PAM 4 chips with a single channel of 1. Gbs 1x. 10. 0Gbs will be available in 2. Optical transmitters based on externally modulated lasers EML, directly modulated lasers DML, and silicon photonics modulators, are becoming available in 2. Linear optical receivers and driver amplifiers, which benefit from coherent optical component development, are also becoming available in 2. Therefore, just like coherent detection is the key solution to long haul systems, we believe that PAM 4 modulation would become one of the key solutions to short haul systems. SimpliFiber Pro Optical Power Meter and Fiber Test Kits are the best firstline fiber testing tool in market. Minimize network downtime with proper installation and. Ethernet Access for Next Generation Metro and Wide Area Networks. Table Of Contents. Ethernet Access for Next Generation Metro and Wide Area Networks. Introduction. Scope. Purpose. Prerequisites. Key Benefits of Metro Ethernet. Challenges. Starting Assumptions. Key Elements. Terminology. Technology Overview. Demarcation Types. Simple Handoff. Trunked Handoff. Service Types. Point to Point Services. Multipoint Services. Design Requirements. Design Overview. Design Topologies. Single Tier Model. Dual Tier Model. Design Considerations. WAN Selection. MPLSInternet. Metro Ethernet. Services. Encryption. Firewall IOSQo. SCapacity Planning. Routing Protocol. Platform Considerations. Access and Midrange RoutersISR and 7. VXR Series. Modular Edge RoutingCisco 7. Series and Cisco ASR 1. Desktop Switches. Scalability Considerations. Overview. Qo. S Configuration. Traffic Classes. Class Map. Remarking. Per Port Shaping. Per Class Shaping. Security Configuration. Intrusion Protection System IOS Firewall. Encryption Algorithms. Scalability and Performance Results. Single Tier Branch. Observations and Comment. Summary. Single Tier Headend. Qo. S Devices for Dual Tier Models. Summary. Case Study. Fairy Tail Soundtrack Vol 5 Download. Existing Topology and Configuration. Branch Router Configuration. Primary Frame Relay Headend Configuration. Secondary Frame Relay Headend Configuration. Revised Topology and Configuration. Branch Router Configuration. Sizing the Metro Ethernet Headend. Metro Ethernet Headend Configuration. Summary. Configuration Examples. Simple Handoff. Headend Configuration7. SIP 4. 00 HCBWFQ per VLANHeadend Configuration7. SIP 4. 00 Per Class Shaper per VLANHeadend Configuration7. SIP 6. 00 Per Class Shaper per VLANBranch ConfigurationTwo VLANs Per Class ShaperDual Tier3. Metro Ethernet Configuration. Bratz Rock Angelz The Game. Troubleshooting. Ethernet LMISNMP Traps. Crypto Logging Session. Appendix. Reference Material. Notes. Cisco Validated Design Ethernet Access for Next Generation Metro and Wide Area Networks Cisco Validated Design July 1. Introduction Scope This document provides design recommendations, configuration examples, and scalability test results for implementing a next generation WAN for Voice and Video Enabled IPsec VPN V3. PN based on a service provider WAN interface handoff using Ethernet at the enterprise campus and branch locations. Purpose This document provides the enterprise network manager with configuration and performance guidance to successfully implement or migrate to a WAN architecture using Ethernet as an access technology to a service provider network. The key to success is the appropriate implementation of quality of service Qo. S on a per branch or per application class per branch technique. In traditional Frame Relay, ATM, and leased line WANs, this Qo. S function is implemented at lower data rates, is limited by the number of physical interfaces or ports that can be terminated in the WAN aggregation router, or is offloaded to an interface processor. Examples of offloading per virtual circuit VC shaping and queueing are the ATM PA A3 port adapter and the virtual IP VIP interface processor with distributed Frame Relay traffic shaping. With current Ethernet access to the service provider network commonly at 1. Mbps or 1 Gbps data rates, the data rate of the user network interface UNI interface is no longer a gating factor. Because this implementation relies heavily on per branch or per application per branch Qo. S techniques, and each instance of Qo. S can be a heavy consumer of CPU resources, the suitability of each platform is a function of the number of peers and the total bandwidth available, as well as the target data rate on a per peer basis. Currently, the access and mid range routers the Cisco 8. VXR Series platforms do not offload to an interface processor, and do not have any means of hardware assistance with implementing HCBWFQ on a per branchpeer basis. However, both the Cisco ASR 1. Cisco 7. 60. 0 offer hardware assistance for Qo. S processing. The Cisco 7. Series implements distributed packet buffering, queueing, and scheduling on certain classes of interfaces Distributed Forwarding Card 3 DFC3 or integrated DFC3 on SIP6. Optical Services Module OSM WAN and SIP 6. Note Regarding the OSM, check with your account team to verify end of sale and end of life announcements prior to implementation. Flex. WAN SIP 2. SIP 4. The ASR 1. Quantum flow Processor QFP, specifically the QFP Traffic Manager to provide hardware processing for Qo. S for all interfaces supported by the chassis. The goal, therefore, is to provide sufficient scale testing to provide conservative estimates of the bounds of the three router platform categories, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Router Platform Bounds The legends on Figure 1 range from 2 5. Mbps aggregate traffic to over 1 Gbps of aggregate traffic. Intermediate hash marks are void as to scale because the performance section provides specific guidance. Finding the most cost effective hardware platform that meets or exceeds the expected offered load with the desired features enabled is a core requirement of all network designs. Prerequisites The target audience is a Cisco enterprise customer deployment. It is not intended as a reference for a service provider offering Metro Ethernet services. Instead, service providers should contact their account team for access to the following documents Metro Ethernet 3. Design and Implementation Guide Metro Ethernet 3. Quality of Service For additional information on V3. PN deployments, the following series of design guides are available at http www. IPsec VPN WAN Design Overview Multicast over IPsec VPN Design Guide Voice and Video Enabled IPsec VPN V3. PN SRND V3. PN Redundancy and Load Sharing Design Guide Dynamic Multipoint VPN DMVPN Design Guide IPsec Direct Encapsulation VPN Design Guide Point to Point GRE over IPsec Design Guide Enterprise Qo. S Solution Reference Network Design Guide Business Ready Teleworker Enterprise Branch Architecture Design Overview Enterprise Branch Security Design Guide Digital CertificatesPKI for IPsec VPNs Key Benefits of Metro Ethernet Metro Ethernet is one of the fastest growing transport technologies in the telecommunications industry. The market for Ethernet is extremely large compared to other access technologies such as ATMDSL, T1E1 Serial, or Packet over SONET POS, making Ethernet chipsets and equipment comparatively low cost. Ethernet provides the flexibility to cost effectively move from 1. Mbps to 1. 00 Mbps to 1 Gbps as an access link, with full duplex FDX 1. Mbps and 1 Gbps Ethernet being the norm. Carriers are more commonly using Ethernet access to their backbone network, whether via SONETSDH, MPLS, Frame Relay, or the Internet. Broadband connectivity is provided by an Ethernet handoff to either a cable modem or DSL bridge.
However, as the internet traffic continues to increase at a 2. G and 4. 00. G optical transceivers are needed. At these higher data rates, the bandwidth provided by a binary optical transmitter or receiver can no longer catch up, and therefore starting in 2. Short haul links, such as intra lt 0. As a result, a simple higher order modulation scheme based on pulse amplitude modulation with four amplitude levels termed PAM 4, has been proposed for either intra or inter data center optical links. PAM 4 is a modulation technique whereby 4 distinct pulse amplitudes are used to convey the information. Amplitude levels 1, 2, 3, and 4 are represented by two bits 0. Each pair of bits is called a symbol. When one of the four amplitudes is transmitted in a symbol period, there are two bits transmitted in parallel, therefore the data rate is doubled. In other words, PAM 4 modulation is twice as bandwidth efficient as conventional binary modulation. Although for a fixed bandwidth, PAM 4 enables twice the transmission capacity in comparison to binary modulation, it has to pay a price of a higher required signal to noise ratio SNR. This is because the additional voltage levels with PAM 4 reduce the level spacing by a factor of 3, and therefore PAM 4 is more susceptible to noise than a binary digital signal. Consequently, PAM 4 is normally used for a short haul optical system where a higher SNR can be obtained. This is also the reason why a higher order modulation such as PAM 8, which has 2. Despite the fact that there are many other modulation techniques that can also double or triple the transmission capacity for a fixed bandwidth, PAM 4 modulation has been a leading solution, mainly due to its simplicity and low power consumption, as the most promising modulation technique for 1. G and beyond optical pluggable transceivers for both intra and inter data center optical links, and a strong PAM4 centric ecosystem is forming. For example, electronic PAM 4 chips based on CMOS technology with two channels of 5. Gbs PAM 4 2x. 50. S157342771400126X-gr1.jpg' alt='Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf' title='Next Generation Optical Networks Pdf' />Gbs is available in 2. PAM 4 chips with a single channel of 1. Gbs 1x. 10. 0Gbs will be available in 2. Optical transmitters based on externally modulated lasers EML, directly modulated lasers DML, and silicon photonics modulators, are becoming available in 2. Linear optical receivers and driver amplifiers, which benefit from coherent optical component development, are also becoming available in 2. Therefore, just like coherent detection is the key solution to long haul systems, we believe that PAM 4 modulation would become one of the key solutions to short haul systems. SimpliFiber Pro Optical Power Meter and Fiber Test Kits are the best firstline fiber testing tool in market. Minimize network downtime with proper installation and. Ethernet Access for Next Generation Metro and Wide Area Networks. Table Of Contents. Ethernet Access for Next Generation Metro and Wide Area Networks. Introduction. Scope. Purpose. Prerequisites. Key Benefits of Metro Ethernet. Challenges. Starting Assumptions. Key Elements. Terminology. Technology Overview. Demarcation Types. Simple Handoff. Trunked Handoff. Service Types. Point to Point Services. Multipoint Services. Design Requirements. Design Overview. Design Topologies. Single Tier Model. Dual Tier Model. Design Considerations. WAN Selection. MPLSInternet. Metro Ethernet. Services. Encryption. Firewall IOSQo. SCapacity Planning. Routing Protocol. Platform Considerations. Access and Midrange RoutersISR and 7. VXR Series. Modular Edge RoutingCisco 7. Series and Cisco ASR 1. Desktop Switches. Scalability Considerations. Overview. Qo. S Configuration. Traffic Classes. Class Map. Remarking. Per Port Shaping. Per Class Shaping. Security Configuration. Intrusion Protection System IOS Firewall. Encryption Algorithms. Scalability and Performance Results. Single Tier Branch. Observations and Comment. Summary. Single Tier Headend. Qo. S Devices for Dual Tier Models. Summary. Case Study. Fairy Tail Soundtrack Vol 5 Download. Existing Topology and Configuration. Branch Router Configuration. Primary Frame Relay Headend Configuration. Secondary Frame Relay Headend Configuration. Revised Topology and Configuration. Branch Router Configuration. Sizing the Metro Ethernet Headend. Metro Ethernet Headend Configuration. Summary. Configuration Examples. Simple Handoff. Headend Configuration7. SIP 4. 00 HCBWFQ per VLANHeadend Configuration7. SIP 4. 00 Per Class Shaper per VLANHeadend Configuration7. SIP 6. 00 Per Class Shaper per VLANBranch ConfigurationTwo VLANs Per Class ShaperDual Tier3. Metro Ethernet Configuration. Bratz Rock Angelz The Game. Troubleshooting. Ethernet LMISNMP Traps. Crypto Logging Session. Appendix. Reference Material. Notes. Cisco Validated Design Ethernet Access for Next Generation Metro and Wide Area Networks Cisco Validated Design July 1. Introduction Scope This document provides design recommendations, configuration examples, and scalability test results for implementing a next generation WAN for Voice and Video Enabled IPsec VPN V3. PN based on a service provider WAN interface handoff using Ethernet at the enterprise campus and branch locations. Purpose This document provides the enterprise network manager with configuration and performance guidance to successfully implement or migrate to a WAN architecture using Ethernet as an access technology to a service provider network. The key to success is the appropriate implementation of quality of service Qo. S on a per branch or per application class per branch technique. In traditional Frame Relay, ATM, and leased line WANs, this Qo. S function is implemented at lower data rates, is limited by the number of physical interfaces or ports that can be terminated in the WAN aggregation router, or is offloaded to an interface processor. Examples of offloading per virtual circuit VC shaping and queueing are the ATM PA A3 port adapter and the virtual IP VIP interface processor with distributed Frame Relay traffic shaping. With current Ethernet access to the service provider network commonly at 1. Mbps or 1 Gbps data rates, the data rate of the user network interface UNI interface is no longer a gating factor. Because this implementation relies heavily on per branch or per application per branch Qo. S techniques, and each instance of Qo. S can be a heavy consumer of CPU resources, the suitability of each platform is a function of the number of peers and the total bandwidth available, as well as the target data rate on a per peer basis. Currently, the access and mid range routers the Cisco 8. VXR Series platforms do not offload to an interface processor, and do not have any means of hardware assistance with implementing HCBWFQ on a per branchpeer basis. However, both the Cisco ASR 1. Cisco 7. 60. 0 offer hardware assistance for Qo. S processing. The Cisco 7. Series implements distributed packet buffering, queueing, and scheduling on certain classes of interfaces Distributed Forwarding Card 3 DFC3 or integrated DFC3 on SIP6. Optical Services Module OSM WAN and SIP 6. Note Regarding the OSM, check with your account team to verify end of sale and end of life announcements prior to implementation. Flex. WAN SIP 2. SIP 4. The ASR 1. Quantum flow Processor QFP, specifically the QFP Traffic Manager to provide hardware processing for Qo. S for all interfaces supported by the chassis. The goal, therefore, is to provide sufficient scale testing to provide conservative estimates of the bounds of the three router platform categories, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Router Platform Bounds The legends on Figure 1 range from 2 5. Mbps aggregate traffic to over 1 Gbps of aggregate traffic. Intermediate hash marks are void as to scale because the performance section provides specific guidance. Finding the most cost effective hardware platform that meets or exceeds the expected offered load with the desired features enabled is a core requirement of all network designs. Prerequisites The target audience is a Cisco enterprise customer deployment. It is not intended as a reference for a service provider offering Metro Ethernet services. Instead, service providers should contact their account team for access to the following documents Metro Ethernet 3. Design and Implementation Guide Metro Ethernet 3. Quality of Service For additional information on V3. PN deployments, the following series of design guides are available at http www. IPsec VPN WAN Design Overview Multicast over IPsec VPN Design Guide Voice and Video Enabled IPsec VPN V3. PN SRND V3. PN Redundancy and Load Sharing Design Guide Dynamic Multipoint VPN DMVPN Design Guide IPsec Direct Encapsulation VPN Design Guide Point to Point GRE over IPsec Design Guide Enterprise Qo. S Solution Reference Network Design Guide Business Ready Teleworker Enterprise Branch Architecture Design Overview Enterprise Branch Security Design Guide Digital CertificatesPKI for IPsec VPNs Key Benefits of Metro Ethernet Metro Ethernet is one of the fastest growing transport technologies in the telecommunications industry. The market for Ethernet is extremely large compared to other access technologies such as ATMDSL, T1E1 Serial, or Packet over SONET POS, making Ethernet chipsets and equipment comparatively low cost. Ethernet provides the flexibility to cost effectively move from 1. Mbps to 1. 00 Mbps to 1 Gbps as an access link, with full duplex FDX 1. Mbps and 1 Gbps Ethernet being the norm. Carriers are more commonly using Ethernet access to their backbone network, whether via SONETSDH, MPLS, Frame Relay, or the Internet. Broadband connectivity is provided by an Ethernet handoff to either a cable modem or DSL bridge.